La Trachéotomie Percutanée par Dilatation est une procédure de routine en Réanimation
La Trachéotomie Percutanée par Dilatation (TPD) est une procédure habituelle réalisée au lit du malade pour les patients sous ventilation mécanique en service de soins intensifs. La bronchoscopie est recommandée pendant la TPD car elle procure une vue directe et améliore la sécurité patient.
Les recommandations cliniques soulignent l'utilisation du monitorage sous bronchoscopie pendant la TPD
La Trachéotomie en soins intensifs est devenue une procédure de routine. Cette tendance se reflète dans les mise à jour des recommandations cliniques soulignants la disponibilité immédiate et le recours au monitorage sous bronchoscopies pendant les procédures de TPD.
La difficulté pour gérer les voies aériennes y compris la trachéotomie percutanée a été la principale cause de morbidité et de mortalité associée à l'anesthésie décrite dans la revue NAP4 de mars 2011. Les résultats recommandent qu'un bronchoscope flexible soit immédiatement disponible en réanimation pour aider à la mise en place de la trachéotomie percutanée ainsi que pour la vérification régulière de la position de la sonde de trachéotomie.
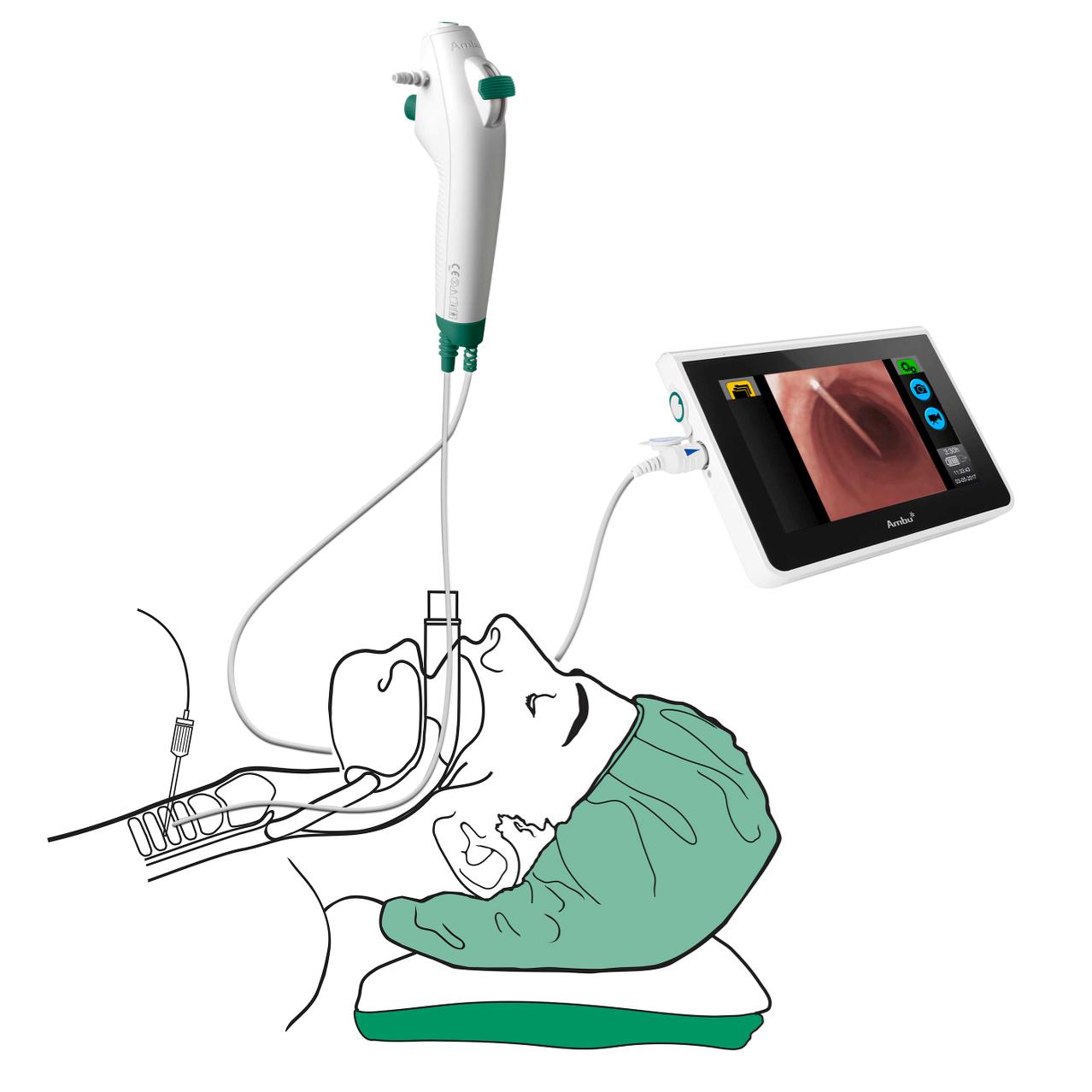
aScope 4 Broncho offre une vue endoscopique claire, permettant à l'opérateur de vérifier la mise en place précise du fil-guide, de l'aiguille et de la sonde de trachéotomie évitant ainsi tout traumatisme au patient.
Worried about damaging your bronchoscope during PDT?
A PDT procedure puts the bronchoscope at risk – in fact 31 hospitals in Germany, the UK and the USA reported that 1 in 27 bronchoscopes was damaged during PDT procedures. That is twice the risk of expected damages for other procedures performed with reusable bronchoscopes.2
Repairs are costly and take time, with high impact on budgets and availability. These damages contribute to an already high cost of working with reusable bronchoscopes where you also have to consider acquisition and reprocessing costs. A study has revealed an average cost of $406 for every PDT procedure conducted with reusable bronchoscopes.2
aScope 4 Broncho is the ideal alternative to reusable bronchoscopes for visual monitoring during PDT procedures allowing you to save $157 per PDT procedure.
+100%*
Augmentation du risque de dommages
$406
Coût moyen par procédure TPD
$157
Economie de coût par procédure TPD2
* Par rapport aux taux de dommages prévus pour d'autres procédures de bronchoscope au chevet du patient
Lire l'article au complet sur SpringerLink pour en savoi plus
aScope 4 Broncho Bénéfices clés
Easy to handle
The lightweight design of aScope 4 Broncho makes it easy to handle and the portability of the aScope system is convenient for bedside procedures in the intensive care unit.
Clear endoscopic view
aScope offers a clear endoscopic view that allows the operator to verify the accurate placement of the guidewire, needle and tracheostomy tube preventing harm to the patient.
Clear cost advantages
The single-use concept has clear advantages in that it eliminates repair costs normally associated with the use of reusable bronchoscopes for PDT procedures. In addition, it increases patient safety as there is no risk of cross-contamination between patients.
aScope 4 Broncho for endoscopic guidance during PDT
aScope 4 Broncho offers a clear endoscopic view, allowing the operator to verify the accurate placement of the guidewire, needle and tracheostomy tube preventing damage to the patient.
Bronchoscopy guidance during PDT is likely to improve patient safety
Bronchoscopy guidance during PDT is likely to improve patient safety as it can guide the correct placement of the introducer needle, the guidewire and the cannula during the procedure.
With bronchoscopy guidance, severe complications such as perforation of the tracheal wall may be avoided.
Bronchoscopy guidance, however, is only one of several factors that improve patient safety during PDT.
According to Simon et al1 when performing PDT, strict consideration of contraindications, bronchoscopy guidance during the entire procedure, an experienced team, avoidance of a low tracheostomy puncture site and avoidance of guidewire kinking, as well as the use of outer flange tracheal cannula sutures are amongst the most important safety factors.
Bronchoscopy guidance during the PDT procedure enhances patient safety
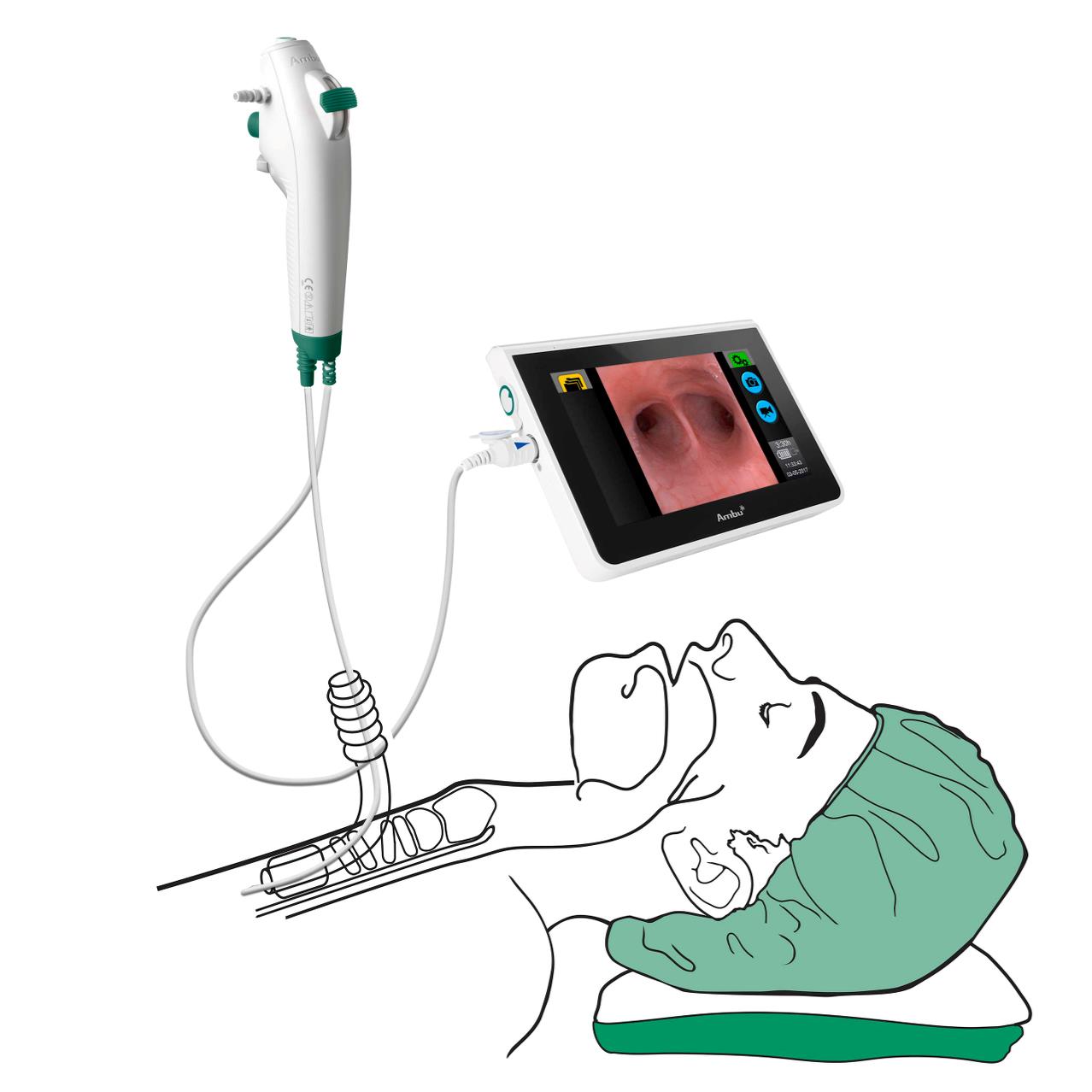
After the PDT procedure, correct placement of the tracheostomy tube is verified.
References
- Simon et al. Death after percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy: a systematic review and analysis of risk factors, Critical Care 2013, 17:R258
- Sohrt, A., Ehlers, L., Udsen, F.W. et al. Cost Comparison of Single-Use Versus Reusable Bronchoscopes Used for Percutaneous Dilatational Tracheostomy. PharmacoEconomics Open (2018)


